
Most state legislative sessions have come to a close for 2019. There are a handful of states that have year-round legislative sessions (MA, MI, NJ, NY, OH, PA, WI), but the majority of 2019 state legislation being drafted has either passed or died. We saw a record number of States this year that have passed electronic prescribing mandates. As of the writing of this blog, 27 of the 50 states have an active or pending mandate!
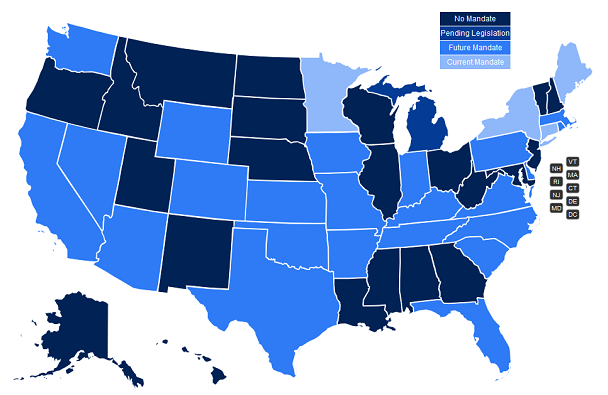
States that have passed a mandate in 2019 are listed below:
States requiring e-prescribing of all prescriptions:
- Florida (7/1/21 or upon license renewal)
States requiring e-prescribing of controlled substances:
- Colorado (7/1/21 or 7/1/23 for solo practitioners)
Two states have enacted amendments to their previously passed mandates. Tennessee has made several major changes to their mandate. The amended Act expands the mandate to cover not only Schedule II drugs, but all controlled substances. The effective date has also been postponed to January 1st, 2020. Arizona has also amended their mandate passed in 2018. Arizona had initially set effective dates of January 1, 2019 for prescribers in counties with populations more than 150,000 and July 1, 2019 for prescribers in rural counties with less than 150,000 residents. The amended mandate has an updated effective date of January 1st, 2020 for all counties in the State.
The majority of states share language in their bills, however there are a few state mandates that contained unique provisions in the wording of their legislation.
- Missouri’s mandate states that electronic prescriptions of controlled substances can be substituted with a written prescription at the direct request of the patient, maintaining an avenue for written prescriptions.
- Florida’s mandate has a provision that allows for practices that exclusively use paper charts to not follow the state mandate requiring electronic prescribing. In speaking with a prescriber in Florida, they were waiting for clarification on this provision before making any prescribing arrangements as the provision’s wording is not entirely clear as to what constitutes an electronic health record as is written in the Act.
- Washington’s mandate requires that medical entities with ten or more prescribers must use an EHR that is integrated with the state Prescription Monitoring Program (PMP) database. The EHR must demonstrate both sending and receiving of PMP data. A waiver process will be made available for this requirement.
- Colorado allows for practitioners who write less than 25 prescriptions for controlled substances per year to not have to adopt electronic prescribing.
Michigan currently has pending legislation for their mandate and is currently being deliberated in committee. There is also an anticipated update to the Ryan Haight act as required per 2018’s SUPPORT Act regarding telemedicine. The deadline established in the SUPPORT Act is October 24th, 2019. Watch our blog or check our social media accounts for any updates regarding either of these legislation changes.
If you reside in any of the states that have enacted mandates this year, MDToolbox encourages prescribers to do their research and adopt a solution early to ensure that they comply with state regulations.
Please see our website for other states that have either passed or have pending legislation that mandates electronic prescribing. MDToolbox looks forward to providing tools and resources to assist providers throughout the United States to ease the transition and help our customers combat the opioid epidemic. With MDToolbox, providers have access to tools such as Electronic Prescribing of Controlled Substances (EPCS) and convenient on the go e-prescribing with our mobile app! We offer a free 30 day free trial, so Contact us for more information!